Fast food operators rushing to use AI in the wake of minimum wage hikes

- Share via
It didn’t take long for Harshraj Ghai to respond to the impact of California’s new $20 an hour minimum wage for his 3,700 fast-food employees.
Ghai and his family operate 180 Burger Kings, Taco Bells and Popeyes chicken restaurants across the state, and one of the first things they did after the law took effect April 1 was to start capping workers’ hours to avoid overtime pay. Also, they’re closing some outlets a little earlier, and opening others a bit later to avoid paying workers for less profitable periods.
But the biggest thing Ghai and his family are doing does not directly involve workers at all: They’ve speeded up and expanded their use of technology, especially AI.
With the state’s mandatory minimum wage for fast-food workers set to increase to $20 an hour, many restaurant chains are preparing to raise prices.
Right now, they’ve moved up by several years their plans to install self-service kiosks at all of their locations, including 25 out of state.
But what has Ghai most hopeful about offsetting the higher labor costs is to have AI handle customers’ orders made at the drive-through. He’s testing the machine-learning system this month at a few locations and hopes to roll it out company-wide by this time next year.

Drive-throughs of course are quintessentially California, with its car culture and fast lifestyle. And now, with AI coming on to the scene in a big way, the state is emerging as ground zero for what many analysts see as the next big thing in the world of fast food and drinks.
Not that AI-led drive-through is quite ready for prime time. As it is today, the system can have trouble with people’s accents and ambient noise, making it hard to recognize speech and translate it into text. Pilot programs run by McDonald’s and others thus far often have backed up the AI technology with an employee, like the Wizard of Oz man behind the curtain. The unseen worker from as far away as the Philippines monitors and sometimes intervenes to complete an order if AI falters.
Even so, Ghai thinks that once the kinks are worked out, it’ll be a godsend for fast-food operators like him.
“It has the potential of being the most impactful,” says Ghai, 39, whose Indian immigrant father, Sunny, started the family business in 1998 by buying a failing Burger King in San Jose, where he was an assistant manager.
What pushed the envelope for businesses like the Ghais’ was California’s sudden 25% hike in the minimum wage for the fast-food industry’s half-million or so workers in the state.
To deal with the big increase in labor costs — which average about one-third of a fast-food store’s sales — many of the affected business owners immediately jacked up menu prices.
Ghai said he’s raised prices overall this year by just 2%. But that’s not been the norm. By the middle of last month, at many franchises across the state — from Jack in the Box to Chipotle to Starbucks — consumers on average were paying a mid- to high-single-digit percentage more than just a month or two earlier, according to a survey by BTIG, the investment banking and research firm.
While the tech industry has been roiled by layoffs, the greater focus on AI could lead to new jobs in the future.
Relatively few appear to have resorted to layoffs, in part because many were already staffed at bare-bones levels. So to hold the line on further price increases, a growing number of fast-food operators are now racing to install as much automation as they can afford.
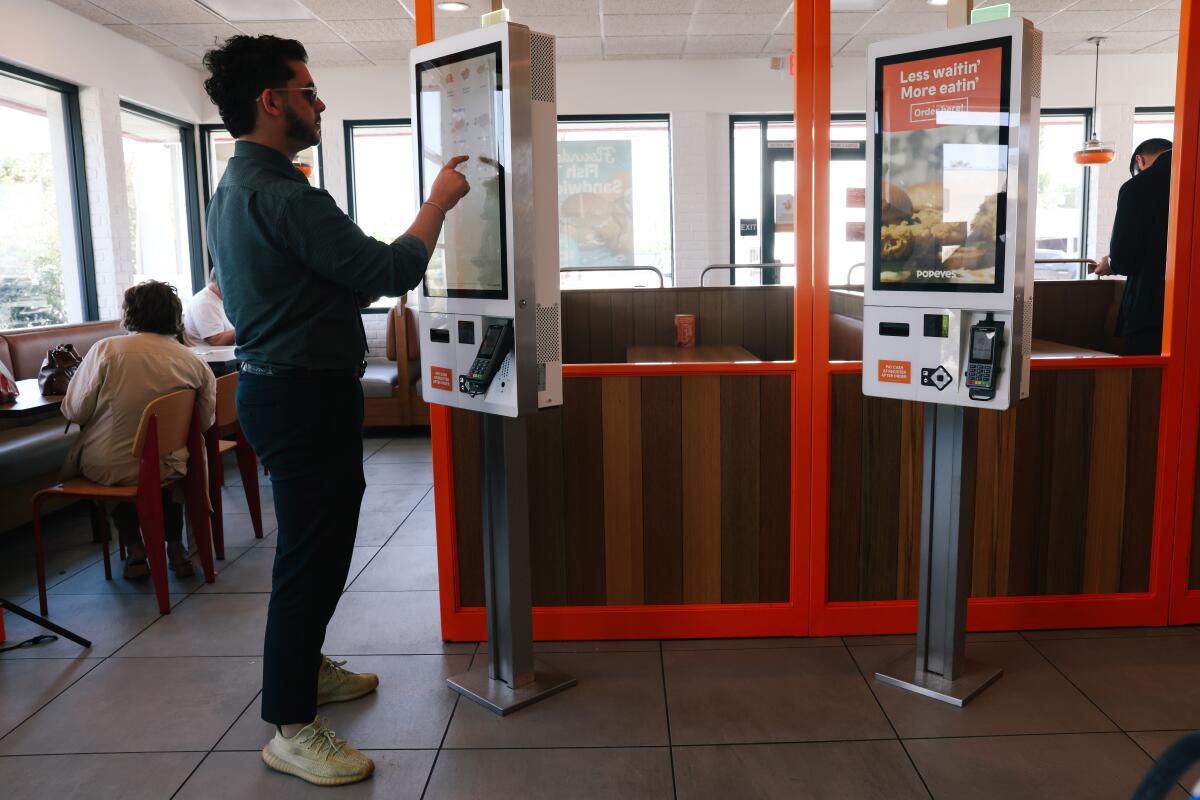
Perhaps the most visible and soon to be widely adopted are all kinds of kiosks for ordering food. The self-service machines have been around for more than a decade, but franchise owners such as Michaela Mendelsohn resisted the move for many years.
“We just didn’t want to force our customers to use technology. We thought the personal contact was important,” said Mendelsohn, who has six El Pollo Loco restaurants in Los Angeles and Ventura counties.
But when the industry’s basic pay rose to $20 an hour, she said, that amounted to $180,000 in additional labor costs a year per store. Within a month of the wage hike, Mendelsohn bought two standing kiosks for each of her six restaurants. That set her back $25,000 per store, for two screens, installation, software and other related costs. One of the two machines accepts cash, which she said was needed for her blue-collar customers.

Mendelsohn figures that the kiosks might save five hours of labor a day. By that estimate, the machines would pay for themselves within a year and shave about 20% of the increased cost from the latest minimum wage increase. “We’re chipping away at it,” she said.
Self-service kiosks are ubiquitous in Western Europe, but they’re in fewer than 20% of fast-food establishments in the U.S., says Perse Faily, chief executive at Los Angeles-based Tillster, one of earliest providers of kiosks and other digital platforms for restaurants.
The COVID-19 pandemic pushed the trend in the U.S., she said, and now in California, “We’re seeing this complete sea change in thinking, ‘How do I address my labor costs?’”
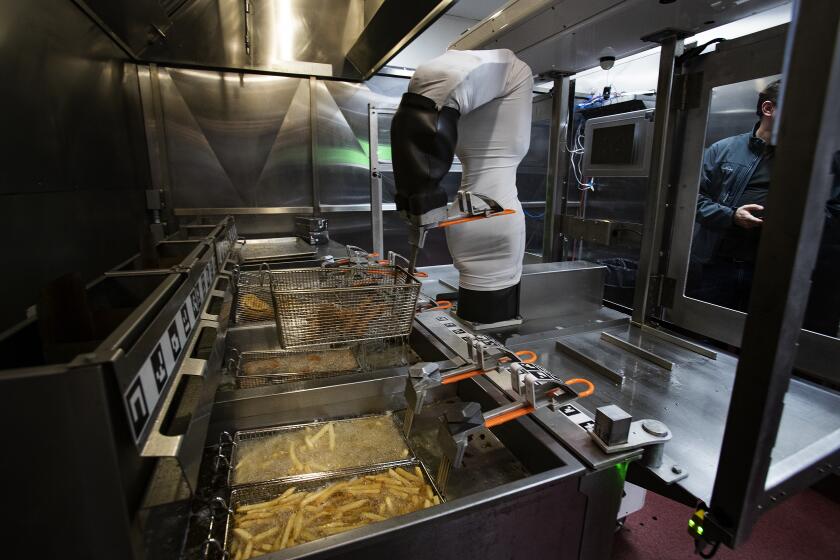
Robotic arms like Flippy from Miso Robotics are getting cheap enough to make financial sense for low-wage work. But there’s an argument in the industry.
Kiosks may be appealing in that they can not only save on labor, but also drive higher sales. Unlike people, the programmed machines are always trying to “upsell,” never forgetting to ask customers whether they want a drink with their meal or something else to go along with their entree.
Faily, Tillster’s CEO since late 2007, wouldn’t disclose the company’s sales increase, but said its new customers include Burger King and Popeyes, and that employment at the firm is up 75 from a year ago, to 340 currently. “The minimum wage increase has completely changed the landscape,” she said.
Other computer-guided upgrades are also aimed at cutting labor costs, from automatic avocado peelers and dishwashers to robotic arms that flip burgers and turn over fryer baskets.
But return on investments, while helpful for the bottom line, don’t do enough to offset burgeoning payroll expenses. So relatively few fast-food operators, for now, are making major investments in robotics and similar mechanical devices.
AI, on the other hand, looks like it could be a game-changer.
The pandemic boosted drive-through traffic at fast-food places to about 80% of sales from two-thirds pre-COVID, said Peter Saleh, a restaurant industry analyst at BTIG. And AI order-taking opens the possibility of speeding up the drive-through process, increasing sales and reducing significant labor overhead.
But analysts say it’s likely to be at least a year or two, maybe longer, before AI-led drive-through reaches a consistent and high enough level of accuracy where companies are comfortable with it. Tests have often left frustrated customers demanding to talk to a live person rather than a bot, according to various accounts.
Major fast-food brands were reluctant to discuss their AI drive-through efforts. Nationally, McDonald’s has been out in front, using an IBM-developed system. A spokesperson would only say that McDonald’s “continues to gather learnings from the roughly 100 pilot restaurants testing automated order taking technology in the U.S. We expect to share more later this year.”
In California, CKE Restaurants, the owner and franchisor of Carl’s Jr. and Hardee’s, appears to be ahead of the pack on the technology, but like other chains, including Taco Bell, Burger King and El Pollo Loco, CKE declined to comment.
Analysts, however, say none of the AI platforms have reached more than 85% success in which human intervention isn’t needed.
“The hardest part is when you have people with accents, from different states and immigrants. It’s challenging,” said Danilo Gargiulo, senior analyst covering restaurants for Bernstein, an investment and research firm.
Still, Gargiulo sees the day when AI will speed up the drive-through line, boosting sales and consumer satisfaction. “Right now the drive-through time is slowed by repeated orders,” he said. With accurate AI speech recognition and faster, clearer communication to the kitchen staff, he said, you can cut as much as 90 seconds off what typically takes 5½ minutes for a customer to complete a drive-through purchase.
That’s what Ghai is betting on.
He says his initial investment for the AI drive-through technology, purchased from San Carlos-based Presto, is about $10,000 per store. Ghai estimates that if he can get it to perform at 90%, a store employee might have to step in to take over an order just three times every hour, freeing up the worker to do other tasks.
The AI system is getting better as it gathers more data, he said, and it’ll soon be able to communicate in Spanish. Add in mobile apps and loyalty programs, and AI has the potential to give fast-food customers a faster and more personalized service. And of course there’s the labor saving part: Ghai thinks the AI drive-through could reduce 10 to 15 hours of wages a day, and double that where he has two human order takers.
“Our goal isn’t to get rid of people. We’re in the people business at the end of the day,” he said. At the same time, Ghai added, over the long haul, “we’ll have fewer people.”
More to Read
Inside the business of entertainment
The Wide Shot brings you news, analysis and insights on everything from streaming wars to production — and what it all means for the future.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.